The GOSTEAM Learning Scenarios
🚀 The GOSTEAM Learning Scenarios
In this lesson, we introduce you to the GOSTEAM Learning Scenarios, a collection of innovative, classroom-ready teaching modules designed to bring STEM, geospatial thinking, and sustainability together in a creative and practical way.
These learning scenarios were developed as part of the GOSTEAM Erasmus+ project, with the aim of supporting teachers in integrating geography, Earth observation, digital tools, and problem-based learning into everyday classroom practice.
✅ What You’ll Learn
✅ Explore the structure and educational value of the GOSTEAM learning scenarios
✅ Discover how each scenario combines geospatial tools, STEM competences, and sustainability themes
✅ Learn how to adapt and implement scenarios to fit different age groups and school subjects
✅ Understand how these scenarios support project-based learning, critical thinking, and creativity
✅ Get inspired to co-create or localize your own place-based, interdisciplinary activities
The GOSTEAM scenarios are designed with flexibility in mind and are applicable in various subjects—from natural sciences, geography, and ICT, to citizenship education and environmental studies. Each one provides a step-by-step guide, digital resources, and assessment tools, making it easy to implement even for teachers new to geospatial thinking or Earth observation. All GOSTEAM learning scenarios are structured using three distinct templates, each tailored to support different teaching and learning environments. This flexible framework allows educators to choose the most appropriate approach based on their classroom goals, student needs, and the nature of the activity.
- The first is the Formal Education Scenario Template, designed for use in traditional classroom settings. It includes clear learning objectives, curriculum alignment, and step-by-step guidance for delivering structured lessons that integrate geospatial and STEM skills.
- The second is the Inquiry-Based Scenario Template, which promotes active student exploration and problem-solving. This approach encourages learners to ask questions, investigate using digital and spatial tools, and draw conclusions—ideal for fostering critical thinking and scientific reasoning.
- Lastly, the Informal Education Scenario Template is tailored for outdoor or experiential learning activities. These scenarios often involve fieldwork, nature-based investigations, and local data collection—making them perfect for applying geospatial thinking to real-life challenges beyond the classroom.
Together, these three templates provide a comprehensive and adaptable framework to support creative, interdisciplinary, and engaging learning experiences across both formal and informal education settings.
👉 Visit the full scenario library here: https://gosteam.eu/scenarios/
Now, let’s explore the potential of these scenarios to transform your classroom into a geospatial innovation hub where students connect science, technology, and sustainability to real-world challenges! 🌍🛰️🔬🧠
Scenario 1: The ancient tunnel of Eupalinos in Samos, Greece (link)
- Target Group: Lower and upper secondary students
- Subjects Involved: Mathematics, History, Geography, Technology
- Number of Lessons: 2-3
- Duration per Lesson: 45’
- Material: Search Engines, Spatial Data, Maps and Online Support Material
- Software: QGIS
This scenario involves different Applied Geometry concepts (angles and orientation, congruent triangles) and Topographic Maps representations (elevation and contour lines) in order to “manipulate” the alignment of the Eupalinos Tunnel which is considered as one of the most important engineering achievements of antiquity. Eupalinos worked as a modern engineer 2500 year ago without using any digital devices, GPS etc., hence, a question arises: “Is it simple to succeed such a task with the use of modern technologies and digital tools?”
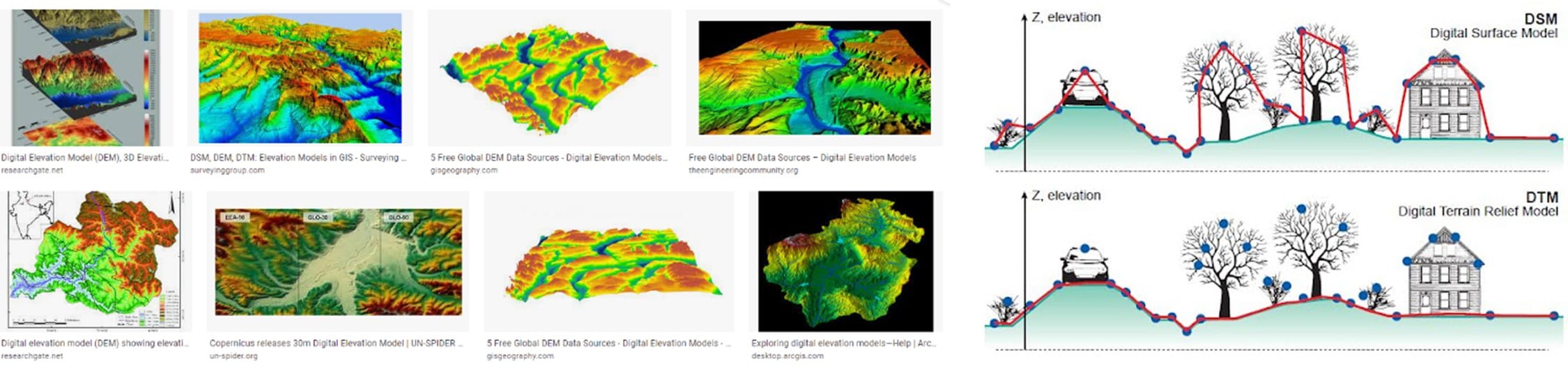
Step 1: Explaining and exploring DEM/DSM and DTM examples and concepts
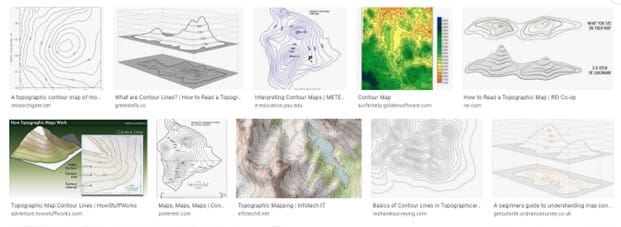
Step 2: Analyzing contour maps examples by simply typing “contour maps on Google”
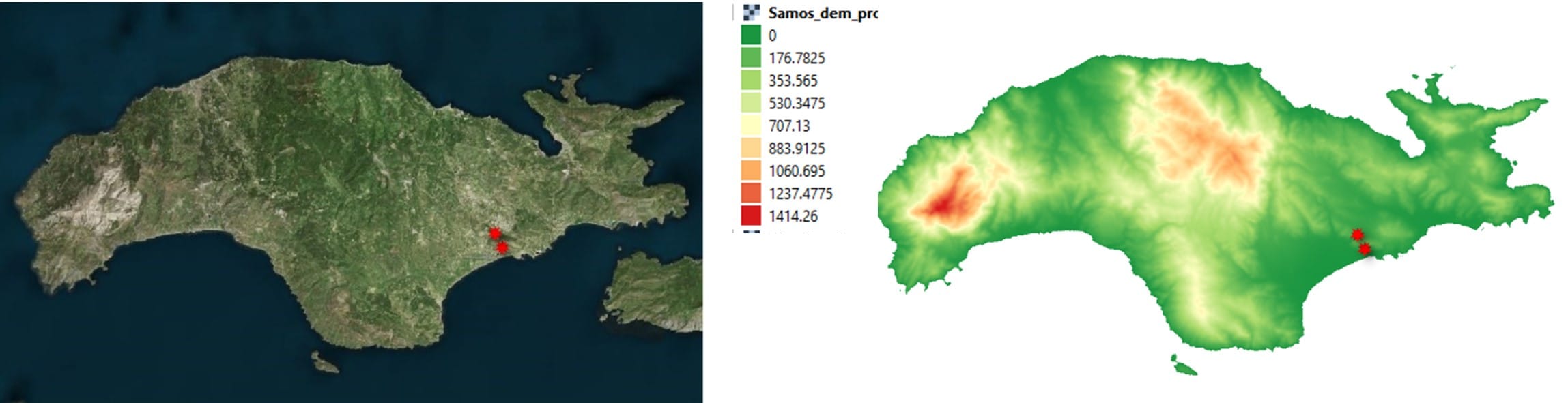
Step 3: Loading satellite images of Samos (left), and downloading the Digital Elevation Model with height values (right)
Step 4: Exporting contour lines of 5 meters interval using Samos DEM
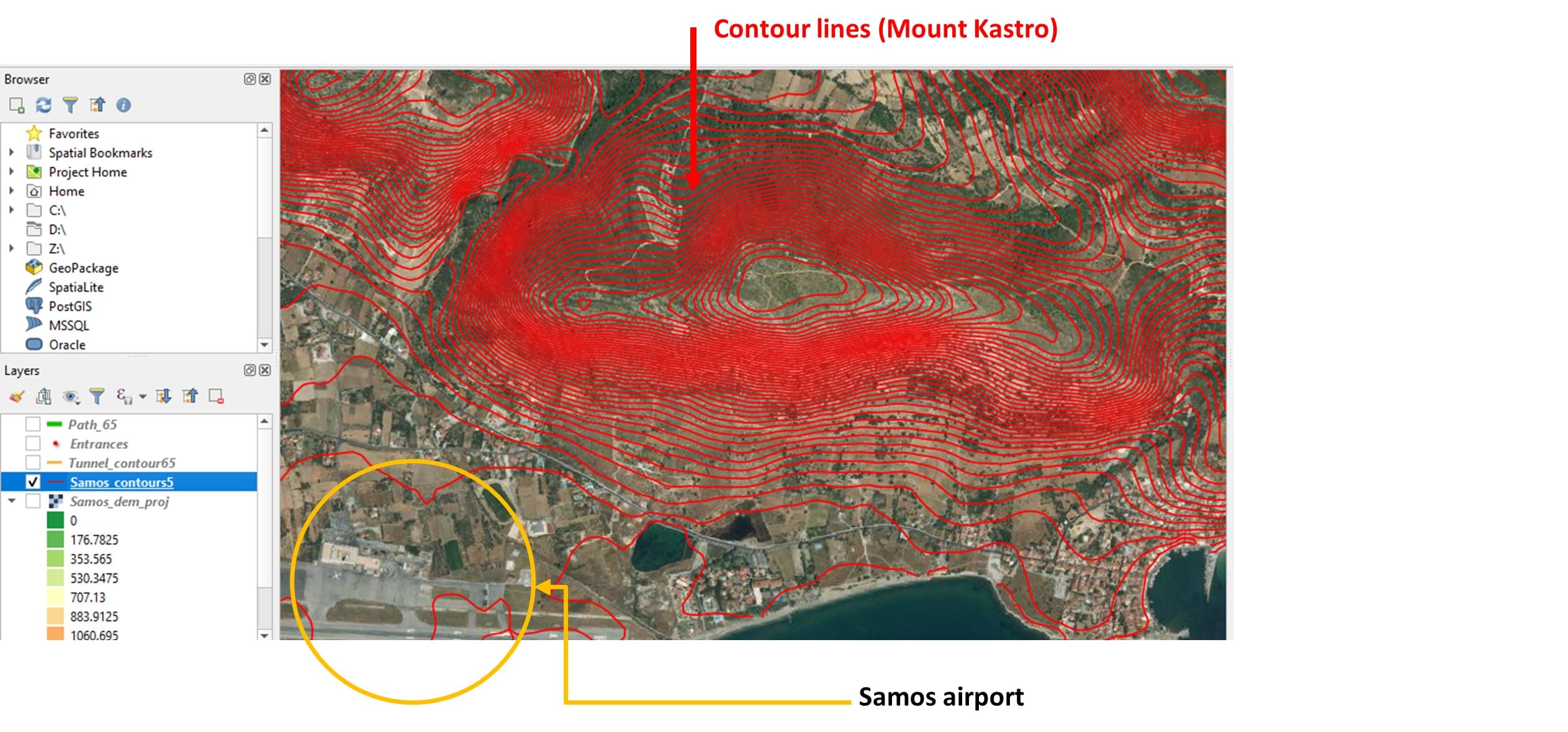
Step 5: Applying Hero’s method for constructing a digitized path for a series of left-angled traverses of same height (approximately)
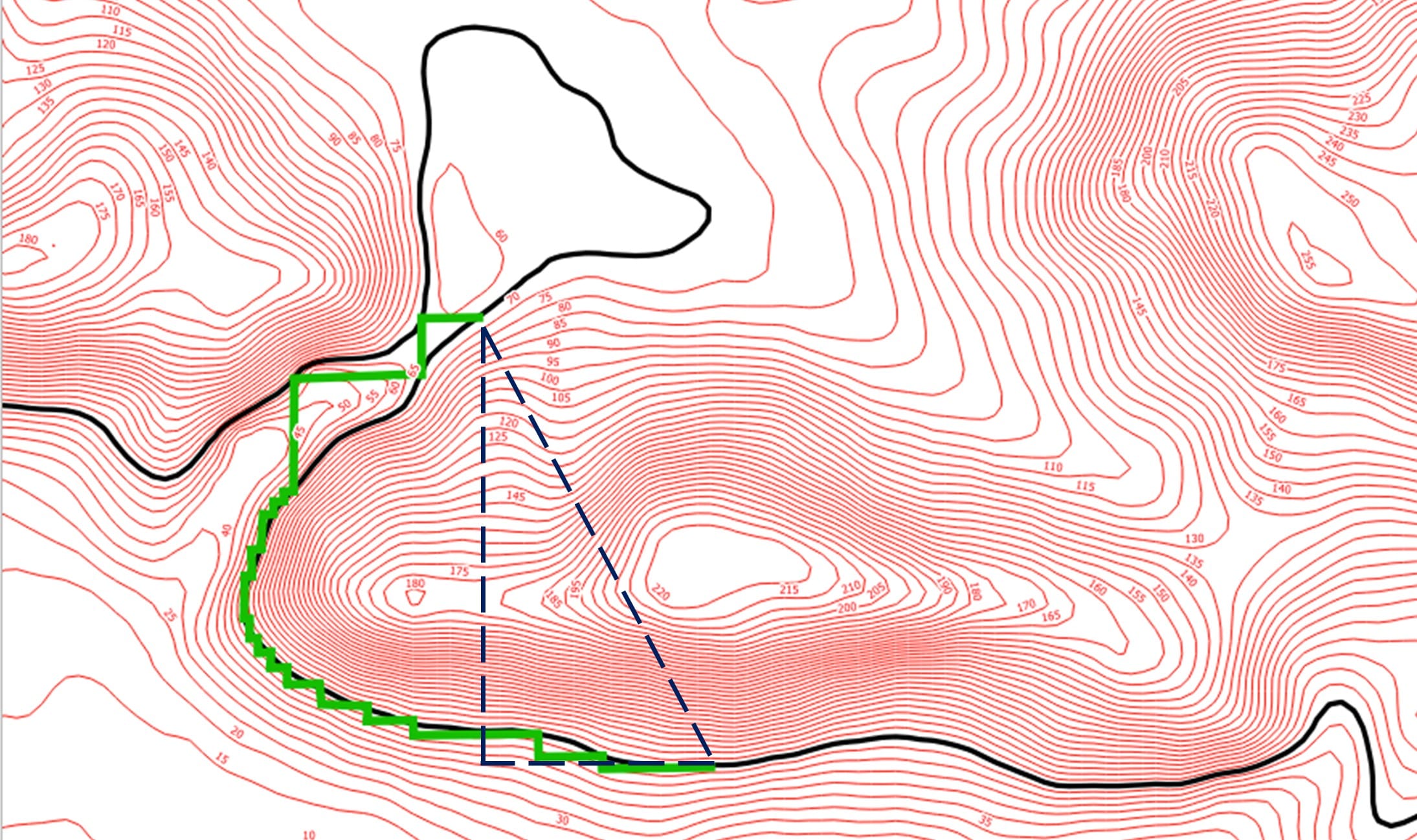
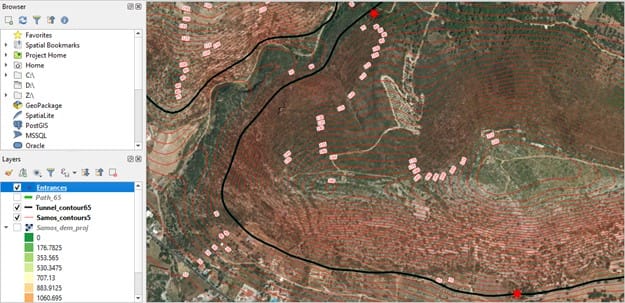
Step 6: Comparing students results with the actual North and South entrance of the Efpalinos Tunnel (red points)
Scenario 2: Potential landing sites on the Moon and Mars for my rover (link)
- Target Group: Lower and upper secondary students
- Subjects Involved: Geography, Technology
- Number of Lessons: 2-3
- Duration per Lesson: 45’
- Material: Search Engines, Satellite Images
- Software: QGIS
Rigorous selection of a landing site for a Martian rover plays a crucial role in the success of the mission because it guides the rover to a location on Mars where the science objectives can be best achieved. Selecting an optimal site is a complex multi-objective optimization problem enumerating a vast number of criteria. During this activity, we focus on certain surface-related parameters, including elevation, latitude and slopes in order to extract an optimal landing sites for a Martian rover! Do you think that’s an easy task? Let’s find out!
Step 1: Discussing on different criteria to identify optimal landing sites on Mars
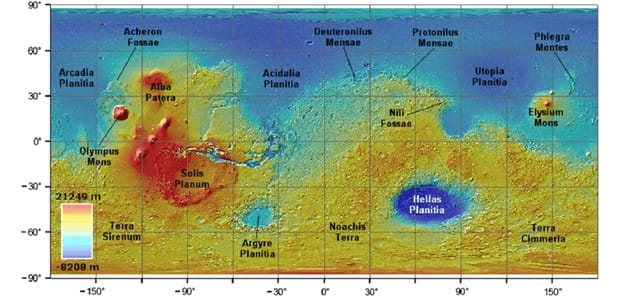
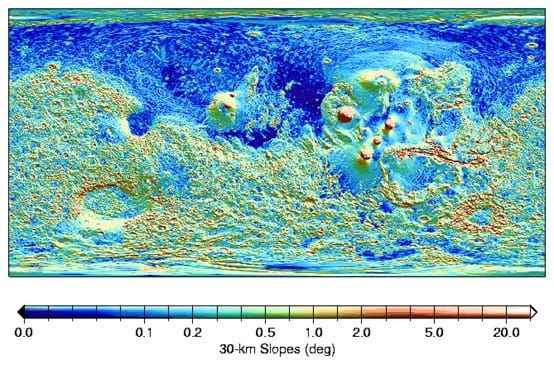

Step 2: Downloading the Digital Elevation Model of Mars and loading it in QGIS Platform
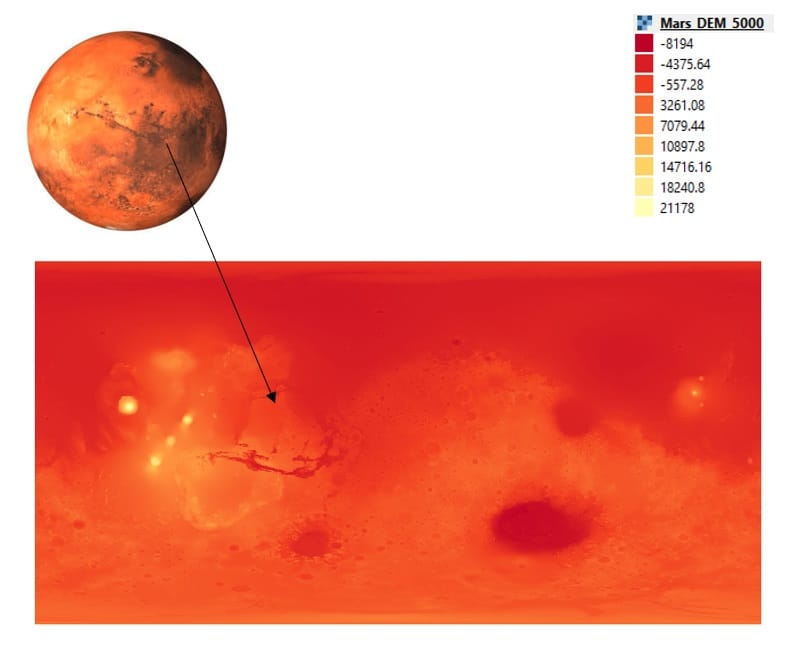
Step 3: Calculating slopes based on Mars DEM via QGIS tools
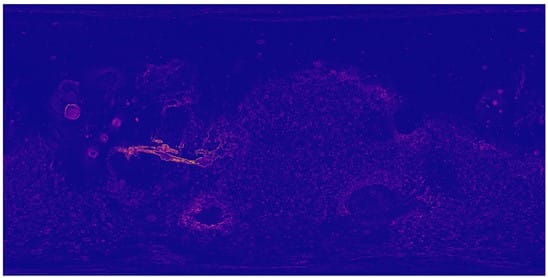
Step 4: Extracting the 3D model of Mars surface using qgis2threejs plugin
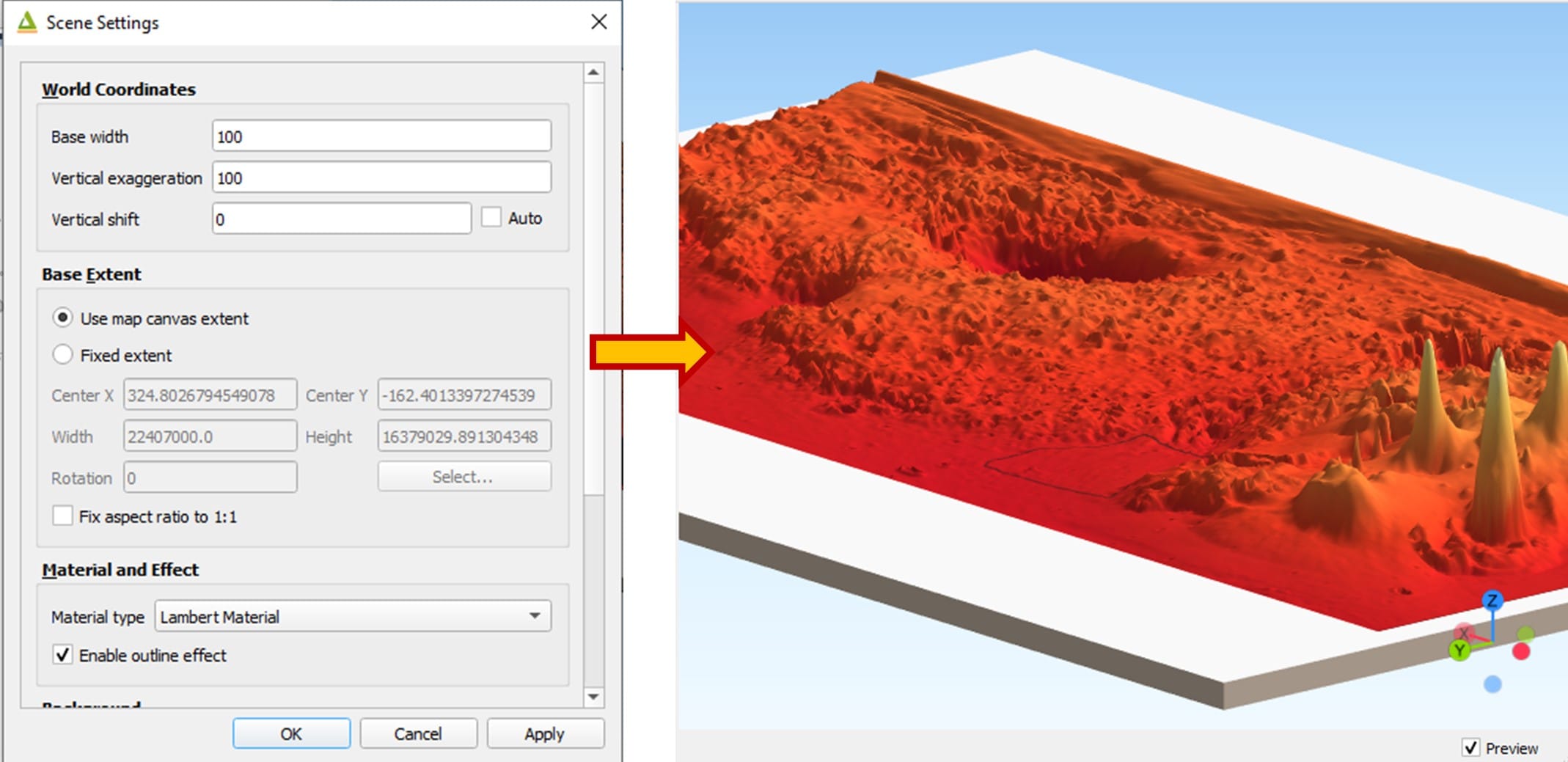
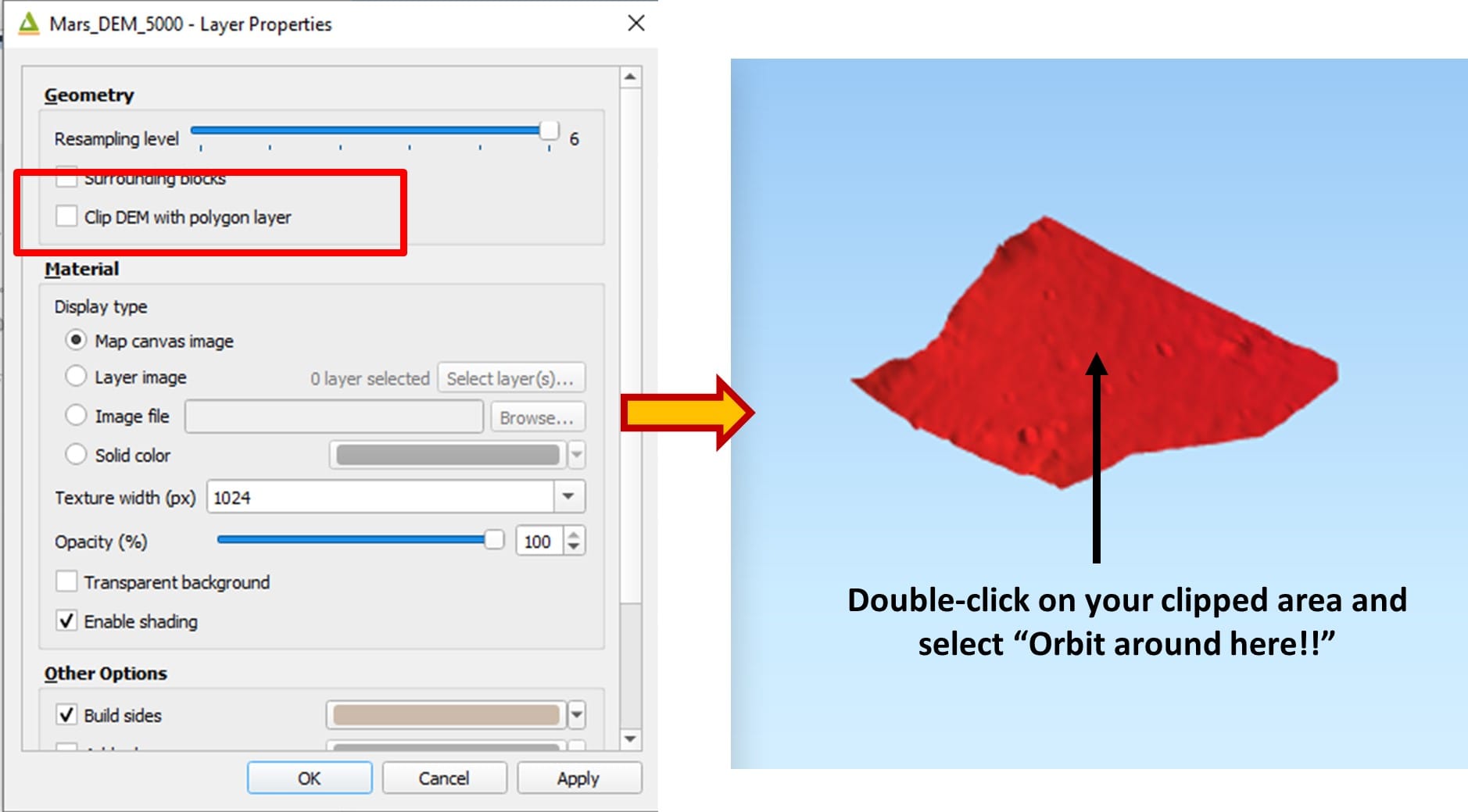
Step 5: Let the students select their optimal area and re-create the 3D model
Scenario 3: Scale of the Solar System in a nutshell (link)
- Target Group: Upper primary school students
- Subjects Involved: Geography, Technology, Physics, Mathematics
- Number of Lessons: 1-2
- Duration per Lesson: 45’
- Material: Search Engines
- Software: Spreadsheet app., FreeMapTools
The best way to appreciate the size of our solar system and the size of the planets is by creating a scaled model of them that shows how far from the sun the eight planets are located (scaled distance). Students will have the opportunity to make these estimates and attribute their findings inside (using digital mapping tools) and outside the classroom (experimentation). Thus, if the sun has the size of your school, where is the earth placed inside your city? Or maybe outside?
Step 1: Shrink/scale the solar system distances and sizes in our city boundaries or our schoolyard (use the excel file in the Additional AMateria section). The fields that the students have to set-up and fill, including the scaled distances and sizes of each planet compared to the Sun’s radius are shown below.
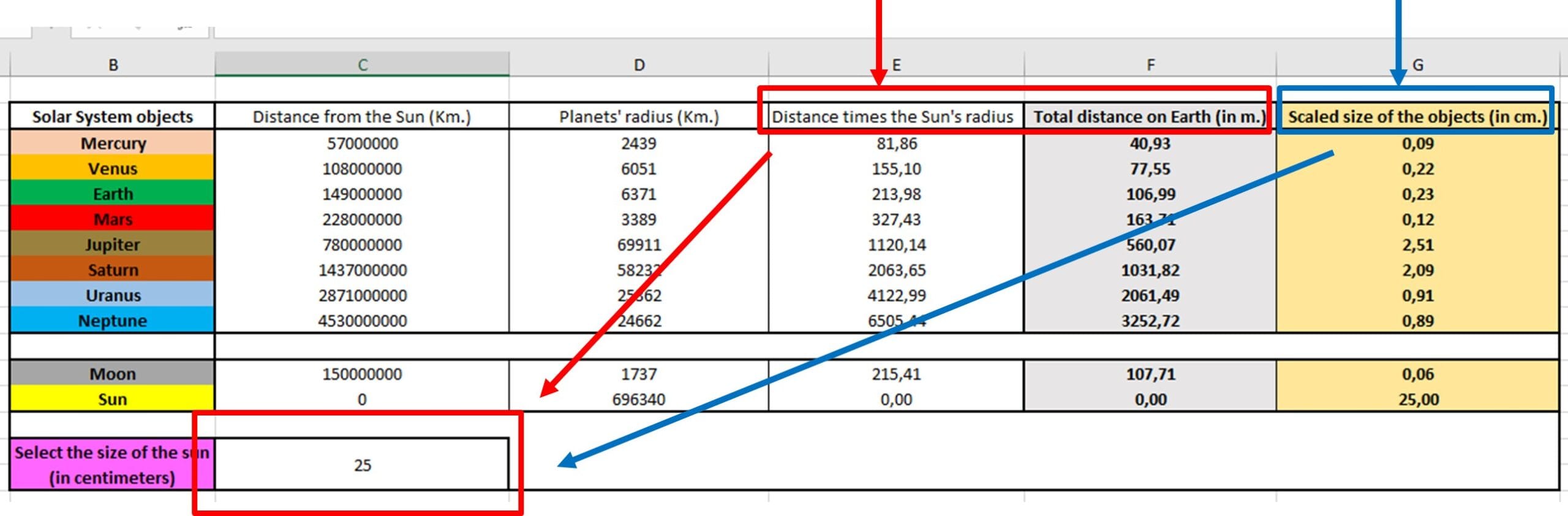
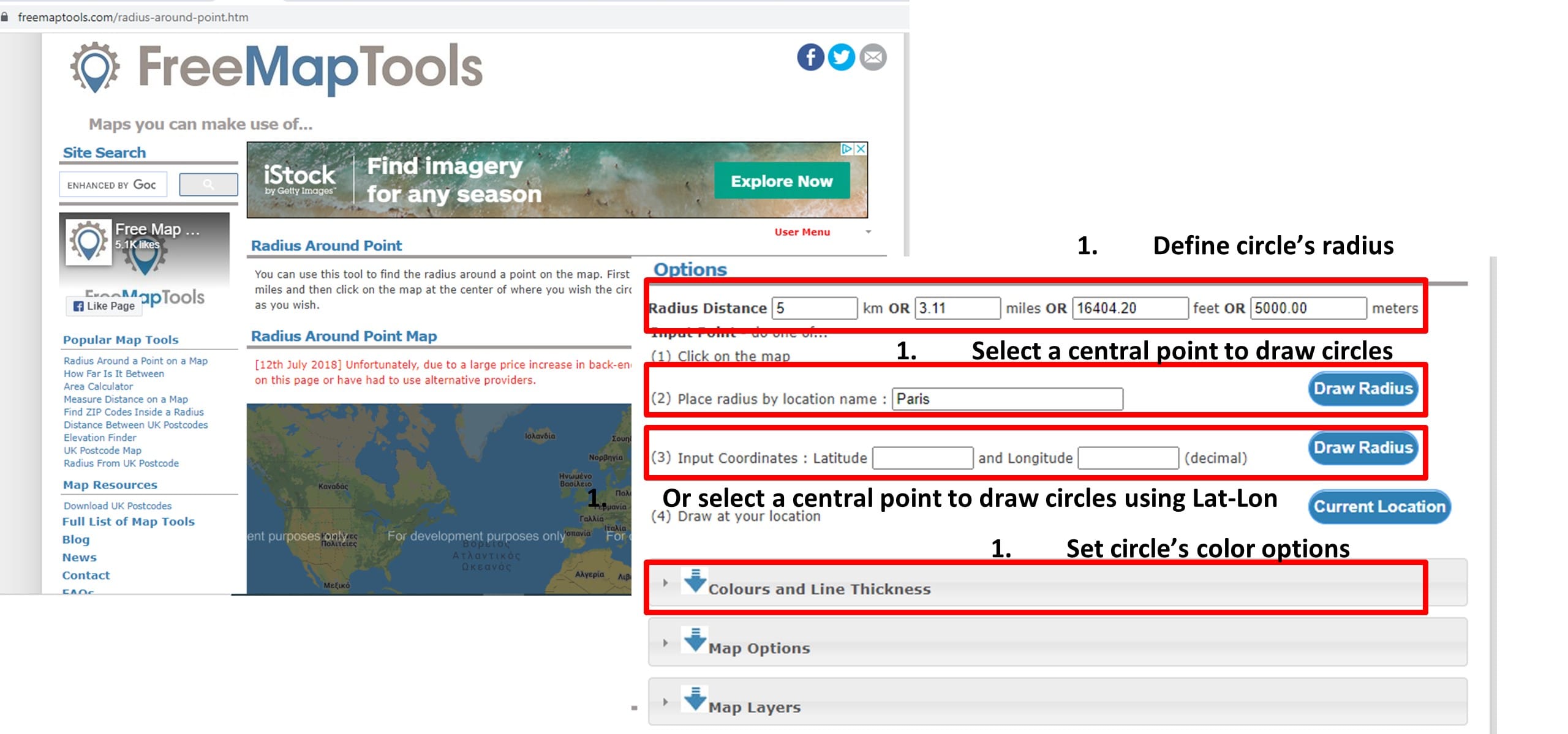
Step 2: Use FreeMapTool to draw planets’ orbits with different colors and size or go outside and use the schoolyard to ‘draw’ the circles or experiment with the distances.
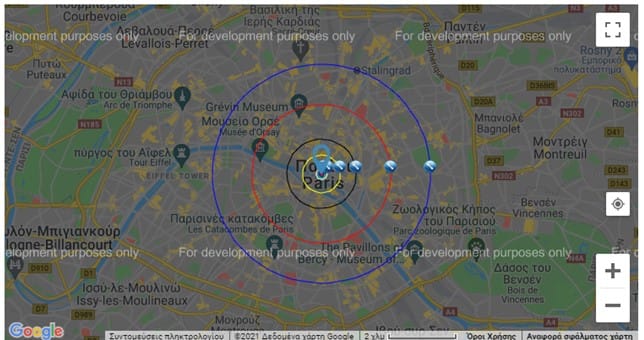
Step 3: Visualize the results (i.e. using Paris metropolitan area) or go outside using printed papers with the planets’ names (see the example here)
Scenario 4: Solar panel placement on Earth (link)
- Target Group: Upper primary and lower secondary school students
- Subjects Involved: Geography, Technology, Physics, Mathematics
- Number of Lessons: 1-2
- Duration per Lesson: 45’
- Material: Search Engines
- Software: Global Solar Atlas
During this activity students learn how the innovative engineering of photovoltaics enables us to transform the sun’s energy into electricity using photovoltaic panels. At first, in this activity we will explain how people use the sun as a renewable energy source for power on Earth as also, how the sun is used as a renewable energy source for power in space missions. Moreover, students will learn about some major criteria and conditions to be addressed in order to select optimal areas for PV solar panels placement on Earth!
Step 1: Discuss on the Earth’s Solar Energy budget and how solar panels work
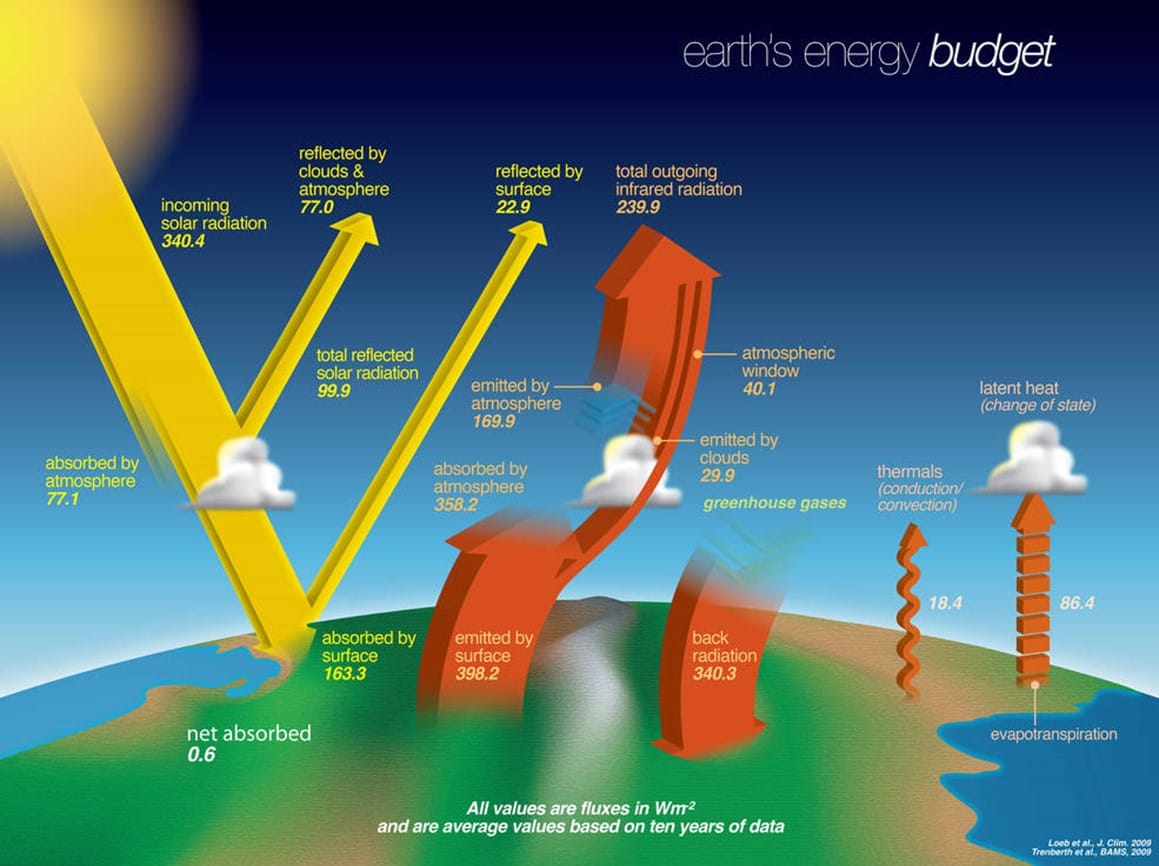
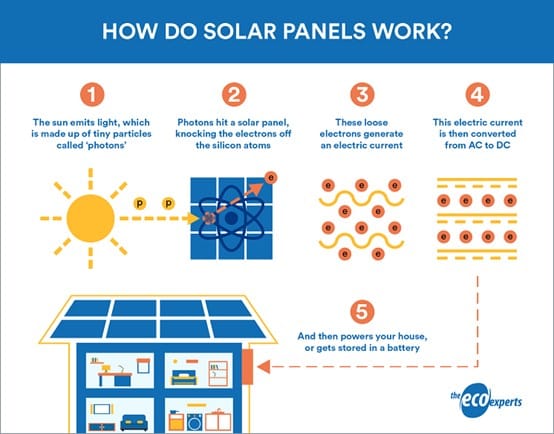
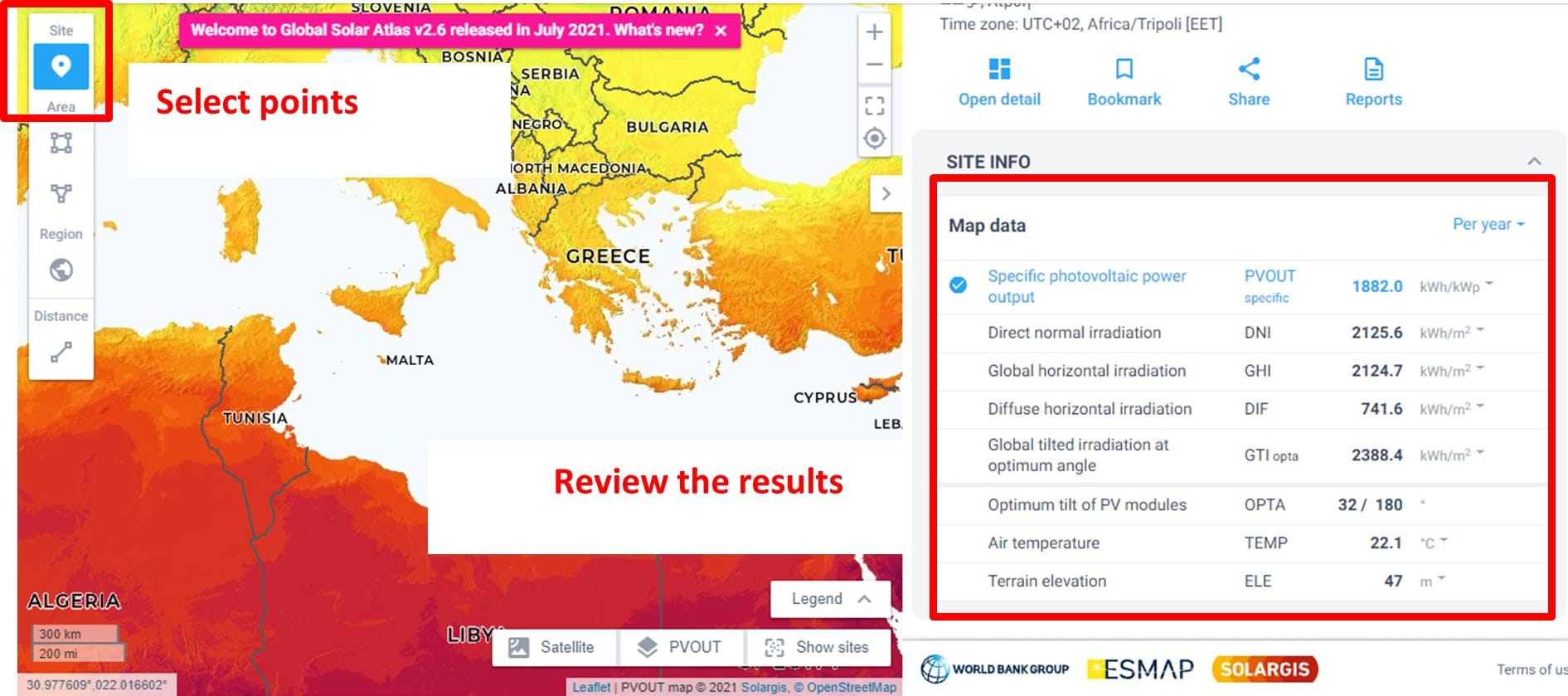
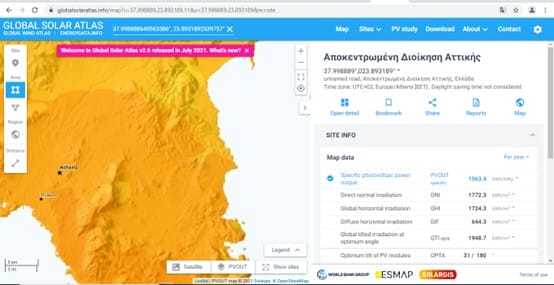
Step 2: Use Global Solar Atlas to calculate and compare the available solar energy potential in different countries worldwide
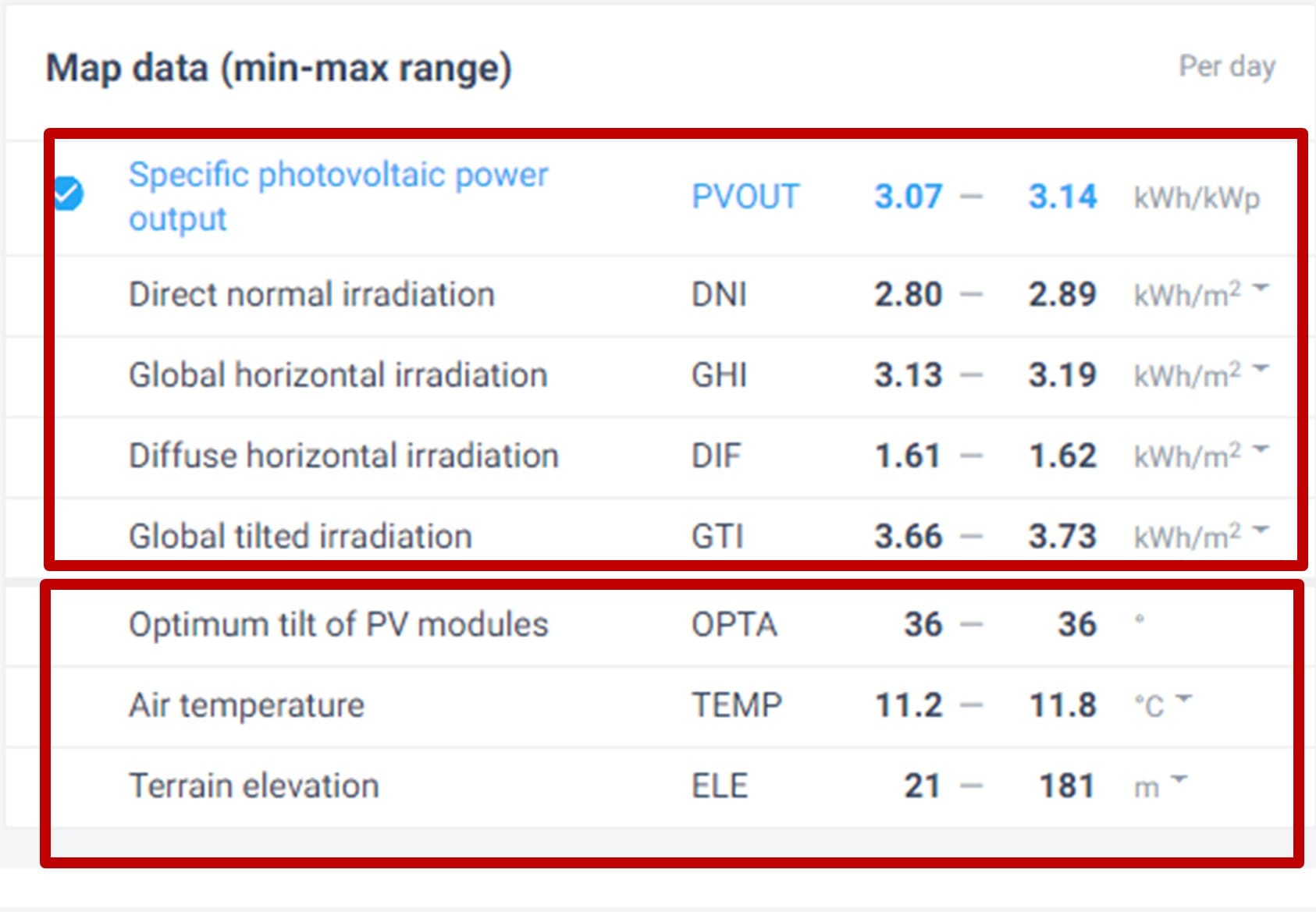
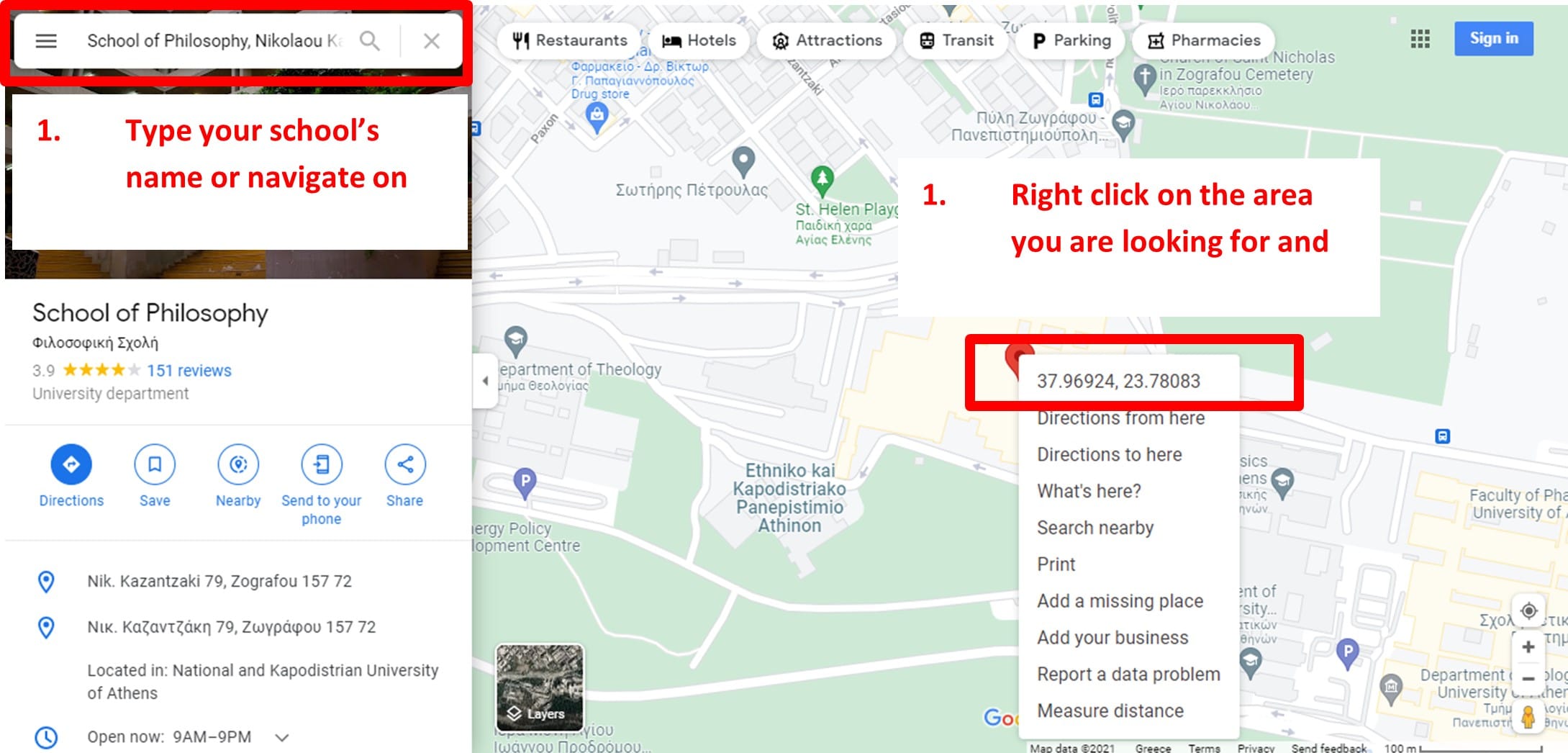
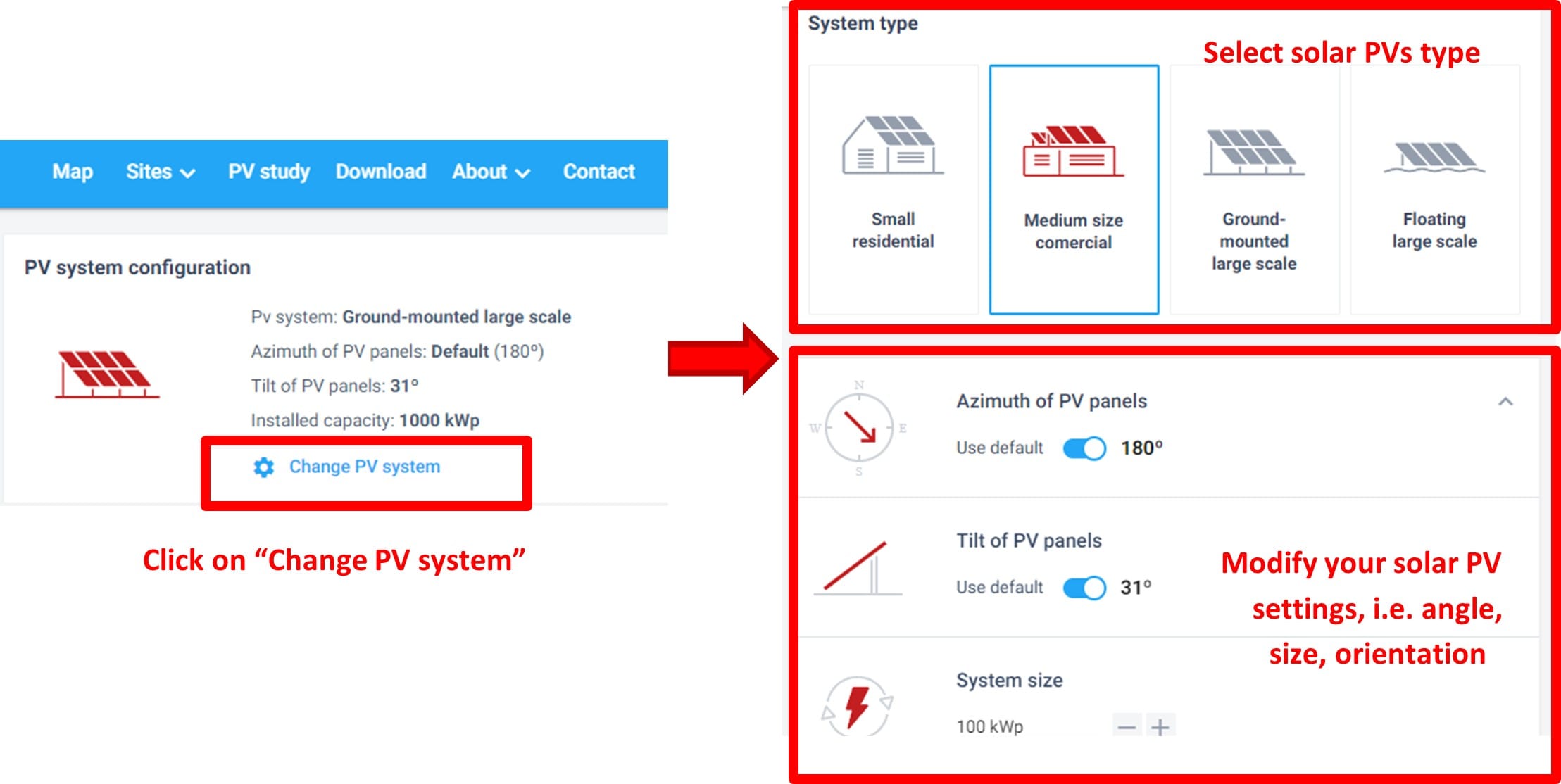
Step 3a: PV Study – Installing solar panels in your school! First we need the exact coordinates of our school
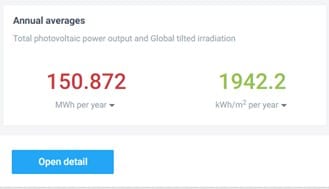
Step 3b: PV Study – Installing solar panels in your school! Estimate the produced energy and the cost!
🎓 Wrapping Up: Explore More GOSTEAM Learning Scenarios
In this lesson, we showcased four inspiring educational scenarios that demonstrate how spatial thinking, STEM education, and sustainability can be meaningfully combined in the classroom using the GOSTEAM methodology. Each example reflects the diversity and creativity of teachers across Europe—and how real-world challenges can become learning opportunities that spark curiosity and innovation.
But this is just the beginning! 🧭
There are many more learning scenarios available that you can explore and adapt to your school context. These activities span subjects such as mathematics, physics, environmental science, engineering, Earth observation, and digital technologies, offering rich opportunities for interdisciplinary, hands-on learning.
Below is a ✨selection of available GOSTEAM scenarios✨—feel free to browse them and find the ones that best fit your teaching goals:
🎨 A new point of view – Tape Art
🪂 Acceleration and gravity in 3-dimensional space
🌊 Applying hydrologic modelling tools to delineate watersheds
📐 Create spatial figures with CAD software
📏 Distances with vector algebra
🌍 Earth Graticule
🛰️ Earth Observation & Satellite images in your classroom
🌱 Ecological Risk Assessment and Satellite observations
🚀 Experiments with PET-powered rockets
📊 Exploring European environmental statistics
📈 Exploring the Eurostat – Statistical Atlas: Economy and Business
🌿 Exploring the Eurostat – Statistical Atlas: Environment and Natural Resources
👥 Exploring the Eurostat – Statistical Atlas: People and Society
📉 Functions in two variables
🏗️ Geodesic dome
🗺️ Google Maps and geographical concepts
🧭 Google Maps Orientation – Basics
🌐 How to use Google Earth
🧾 Introduction to map projections
💡 Light Paintings
🌧️ Mapping flooded area using radar satellite remote sensing
🔍 Mirror Anamorphosis
🌍 Monitoring drying inland water bodies using satellite remote sensing
👁️ Optical illusions
🛣️ Optimal route finding and Least Cost Path concepts
🌕 Potential landing sites on the Moon and Mars for my rover
☀️ Scale of the Solar System in a nutshell
🌊 Sea level rise impact on coastal areas
🔆 Solar panel placement on Earth, the Moon, and Mars
🏛️ The ancient tunnel of Eupalinos in Samos, Greece
🗾 The Map of the Island
📡 Trilateration and the GPS
🌄 Work with digital elevation models (DEM)
🌇 Shadows and heights
🌌 Celestial coordinates
🧭 The Orthodromic Routes
🌍 Epicentral location
🌐 The measurement of Earth’s radius (Eratosthenes method)
❄️ The glacial seas from space
🌡️ The greenhouse effect and its consequences
🏞️ Topographic profiles
🤖 Rover exploration game developed with Scratch
🌬️ Selecting an Offshore Wind Farm site
Feel free to continue your journey through the GOSTEAM library and bring geospatial thinking and creative problem-solving into your own classroom!
